Projects
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Yaseen designed a compact, synthesizable RV32I-style RISC‑V core implemented in Verilog. The design contains a simple program counter, register file, ALU, control unit, and synchronous instruction/data memories designed to infer Intel M9K BRAMs. The repository includes reusable RTL components (muxes, adders), a small testbench suite compatible with ModelSim and Verilator, and documentation for Quartus-based FPGA builds.
Verification used directed testbenches and waveform inspection to validate instruction execution. An OpenLane flow was used to generate a GDS II layout, demonstrating an end-to-end path from RTL to a fabrication-ready layout.
Verification used directed testbenches and waveform inspection to validate instruction execution. An OpenLane flow was used to generate a GDS II layout, demonstrating an end-to-end path from RTL to a fabrication-ready layout.
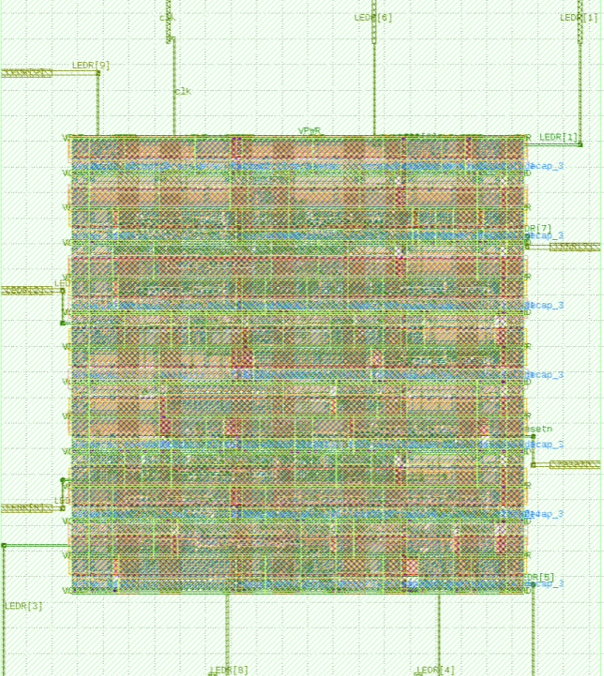
RV32I-style core: RTL → FPGA → OpenLane GDS
Yaseen implemented a minimal but functional RISC-V RV32 microkernel that boots in machine mode on QEMU's virt platform. The project demonstrates a complete bare-metal system including hand-written entry and trap assembly, timer interrupts, preemptive round-robin scheduling, kernel threads with dedicated stacks, Sv32 virtual memory, a bump-based physical memory allocator, synchronization primitives (spinlocks and semaphores), and a timestamped UART logger. It includes a basic syscall interface (ECALL-based yield) with cooperative and preemptive scheduling demo threads.
The kernel showcases full register save/restore with trap frames, a CLINT timer driver with 10 ms tick programming, automatic GP setup for kernel threads, and an identity-mapped Sv32 page table. The repository is suitable for exploration of bare-metal systems and low-level RISC-V platform software.
The kernel showcases full register save/restore with trap frames, a CLINT timer driver with 10 ms tick programming, automatic GP setup for kernel threads, and an identity-mapped Sv32 page table. The repository is suitable for exploration of bare-metal systems and low-level RISC-V platform software.
Technologies: RISC-V Assembly, C, QEMU, Machine-mode, Virtual Memory, Scheduling
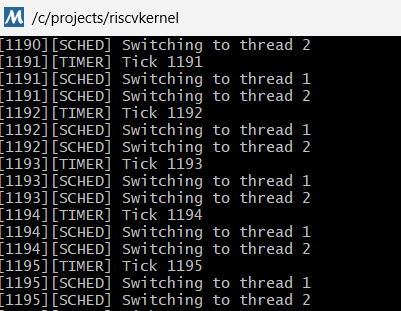
RV32 Microkernel: machine-mode boot, scheduler, and virtual memory
Real-Time Hardware Video Processing System
In Progress
Yaseen developed a real-time hardware video processing system for the Terasic DE1-SoC board using a D8M-GPIO camera and VGA video interface. The project includes multiple video processing functions implemented in Verilog, with a focus on pipelined architectures, memory management, and hardware optimization.
The system implements an "old film" effect processor using grayscale conversion, random vertical black lines, random black splotches, and original effects implemented with LFSR-based random number generation. It also includes convolutional 2-dimensional blurring filters with 3×3 and 11×11 kernel sizes, designed to process video at real-time frame rates.
The project emphasizes baremetal C programming on the embedded HPS processor for bit-accurate software implementations, alongside comprehensive ModelSim testbenches and golden reference models. Design work includes detailed pipelined block diagrams, timing analysis, arithmetic optimization, and performance characterization through maximum clock rate, throughput, and latency measurements.
The system implements an "old film" effect processor using grayscale conversion, random vertical black lines, random black splotches, and original effects implemented with LFSR-based random number generation. It also includes convolutional 2-dimensional blurring filters with 3×3 and 11×11 kernel sizes, designed to process video at real-time frame rates.
The project emphasizes baremetal C programming on the embedded HPS processor for bit-accurate software implementations, alongside comprehensive ModelSim testbenches and golden reference models. Design work includes detailed pipelined block diagrams, timing analysis, arithmetic optimization, and performance characterization through maximum clock rate, throughput, and latency measurements.
Technologies: Verilog, Quartus, ModelSim, DE1-SoC, VGA, D8M-GPIO, Baremetal C, HPS
Real-time hardware video processing system on Terasic DE1-SoC
Hardware FIFO Design
Yaseen designed a parameterized FIFO in Verilog using dual-port M9K memory blocks on the DE10-Lite FPGA. He created read and write modules operating at different clock frequencies to demonstrate clock-domain crossing (CDC) data transfer and verified functionality through ModelSim simulations and Quartus synthesis results. The implementation uses a circular FIFO architecture with full and empty condition detection and was tested across multiple clock-domain scenarios.
Technologies: Verilog, ModelSim, Quartus, DE10-Lite, M9K Memory, Clock Domain Crossing
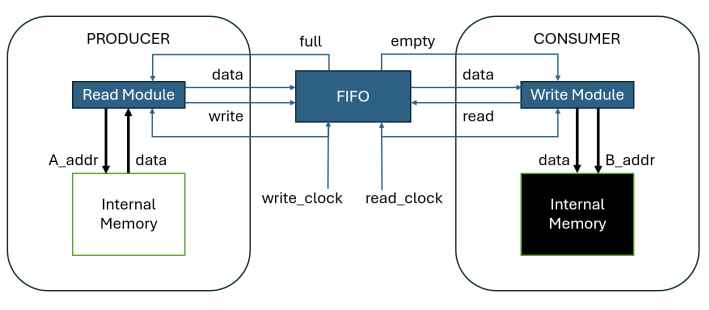
Parameterized FIFO with dual-port M9K memory and clock-domain crossing
FPGA Dice Game
Yaseen implemented Moore and Mealy finite state machine representations of a dice game using RTL and block schematics. He applied sequential network design through implementation of counters and memory and verified the design using Verilog testbenches and ModelSim, then demonstrated the design on the DE10-Lite FPGA.
Technologies: Verilog, ModelSim, Quartus, DE10-Lite, FSM Design
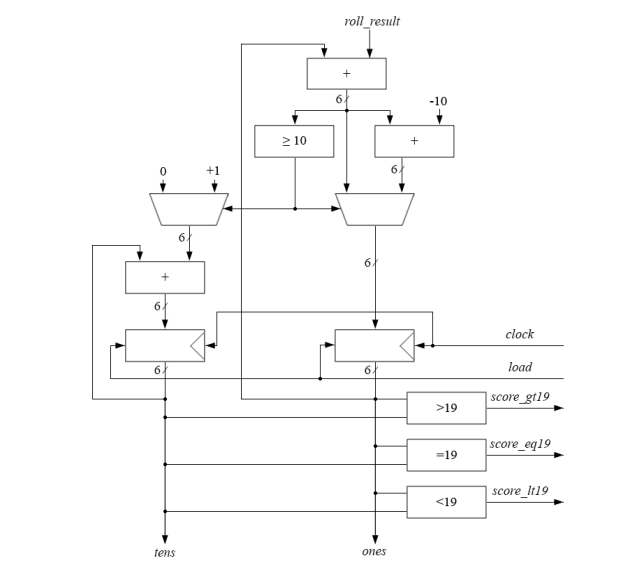
Schematic of Score Processing and Display Circuit
Built during AgentHacks with teammates, dExtra Tools extends the Dex browser agent by adding a Working Memory system, a Planning Agent, and a Frontend-WebSocket bridge (get_selected_text). The system integrates with an MCP backend and enables deeper, real-time browser interaction for agent workflows. Won Dex Best Browser Agent at AgentHacks.